A recent finding shared by the scientists from the University of Bristol in the UK can help science explain how pericytes, the cell which encircles blood vessels, are able to support the formation and growth of new blood cells with the help of leptin.
In case you didn’t know, leptin is a hormone formed by fat cells and its basic role is to help manage energy balance in the system by blocking our appetite.
The scientific study presented in Scientific Reports may be useful in the process of treating heart attacks and cancer, two diseases that are affecting millions of people around the globe.
The formation and thriving of new blood cells known as angiogenesis is an essential process that is present in both disease and health. For instance, it supports the progress of cancer, but it also speeds up the process of tissue repair after an injury.
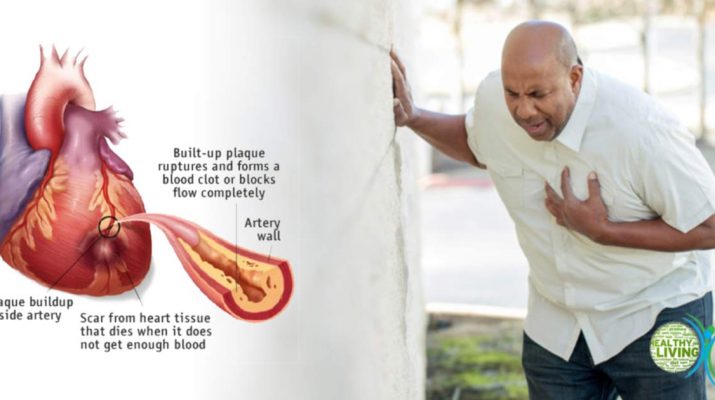
Today, one of the main heart attack treatments is a surgery known as coronary artery bypass. Doctors are using blood vessels obtained from the leg, or some other body parts, to bypass the clogged artery and boost blood flow to our heart.
Keep in mind that this is a highly invasive and complicated surgery that requires a lot of time for recovery. So, the discovery we’ve mentioned before may serve as a starting point for an alternative treatment of heart attacks.
What’s important is that the team of specialists has discovered that pericytes were able to create up to 40 times more of the hormone leptin after an exposure to relatively low levels of oxygen. This is an ongoing process until the exposure to oxygen is stopped.
In this way, it is possible to support tissues’ efforts to create more blood vessels to boost oxygen supply and blood flow.
This finding, as well as few other findings, have shown that leptin is involved in a few essential actions which support the growth of brand new blood vessels in places where tissues were not receiving enough oxygen.
In the vast majority of cases, a heart attack occurs after a complete inhibition of a coronary artery. The inadequate supply of blood to the heart muscle usually results in a damaged heart.
The team of scientists led by professor Madeddu has confirmed that by supporting new blood vessel growth, these pericytes have the ability to bring back blood supply to the affected heart muscle after the person experiences a heart attack.
According to Paolo Madeddu, a respected professor of experimental cardiovascular medicine who works at the School of Clinical Sciences and the team leader of the project conducted by the Bristol Heart Institute, the latest breakthrough they’ve made may serve as an excellent starting point for a new, more effective heart attack treatment.
In addition, he believes that this discovery can help cancer patients too. The results have shown a new mechanism for sending signals that have a potential to affect cardiovascular regeneration.
Barbara Harpham, CE of Heart Research UK, said that boosting leptin in pericytes in a recovering heart may accelerate the healing process.
On the other hand, inhibiting leptin production in cancer-affected pericytes can starve the tumor and make it shrink. She also said that this latest research project has provided results that can help patients right away.
Source: Medical Xpress