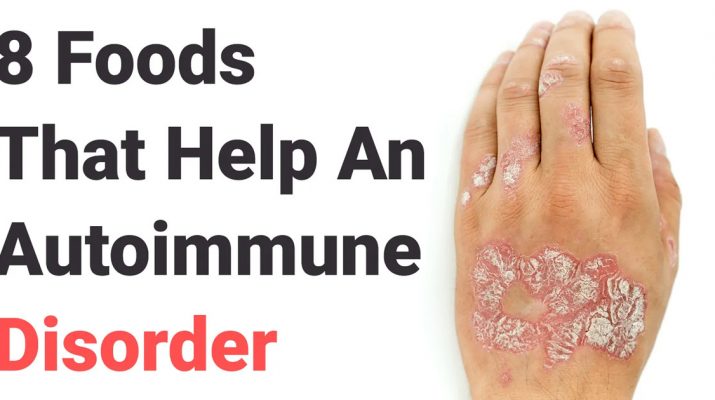
It is the job of the immune system to protect us from infection and disease. But for people with an autoimmune disorder, the very system responsible for keeping them healthy turns on them. Instead of an immune system that protects them from illness, they have an immune system that may cause illness.
Common autoimmune disorders include celiac disease, diabetes type 1, Graves’ disease, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), multiple sclerosis (MS), psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus. By no means is this list all-inclusive. According to the Office on Women’s Health, there are an estimated 80 different types of autoimmune diseases, affecting nearly 24 million Americans.
Common symptoms of autoimmune diseases include:
- Extreme fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
- Muscle pain
- Numbness and tingling
- Low-grade fever
- Hair loss
- Skin dryness and skin redness
The common denominator behind every autoimmune disorder is chronic inflammation. As we’ve discussed many times before, the foods we eat play a significant role in our inflammation levels. On that note, we’re going to talk about foods that reduce inflammation and also help alleviate the symptoms of autoimmune disorders.
Here Are 8 Foods That Help An Autoimmune Disorder
“It is becoming increasingly clear that chronic inflammation is the root cause of many serious illnesses – including heart disease, many cancers, and Alzheimer’s disease.” – Dr. Andrew Weil (source)
1. Halibut
One small portion of halibut contains an entire day’s worth of vitamin D. A lack of “D” is linked to a number of autoimmune diseases, including lupus, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Other fish sources of vitamin D include mackerel, salmon, sardines, tuna, and whitefish. Vegetarian sources include egg yolks and organic mushrooms.
2. Turmeric/Curcumin
Various studies conclude that the main ingredient in turmeric, curcumin, encourages immune system health through its anti-inflammatory properties. Per the Arthritis Foundation, curcumin suppresses the symptoms of both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, including inflammation, joint pain, and joint stiffness.
A more bioavailable form of curcumin, called nano-curcumin, has even been approved in some countries as a legitimate treatment for HIV/AIDS and cancer.
3. Broccoli
Broccoli contains a potent antioxidant called glutathione, which may help alleviate the symptoms of autoimmune diseases. Glutathione is a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant that has been shown in some studies to be at deficient levels in people with an autoimmune disorder.
Cauliflower, cabbage, kale, onions, radishes, and other foods high in sulfur also contain glutathione.
4. Flaxseed
Flaxseed is a favorite among vegans and vegetarians for its high omega-3 content. Per a study published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition, omega-3s contain “the most potent immunomodulatory” properties of any fatty acid. Many clinical trials attest to the benefits of omega-3 supplementation in relieving some of the most common types of autoimmune diseases, including Crohn’s disease, lupus, multiple sclerosis, and psoriasis.
5. Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut is an excellent source of probiotics, which help to balance the gut’s levels of good and bad bacteria, or microbiome. When the microbiome is healthy, our gut is less prone to permeability, a condition known as “leaky gut.” In turn, we are less susceptible to an autoimmune disorder and related symptoms. Other good sources of probiotics include fermented veggies, kimchi, pickled ginger, and kefir.
6. Green Tea
Preliminary studies examining the effect of green tea on autoimmune diseases show tremendous promise. Researchers believe that green tea, due to its effect on specialized immune cells (or “T-cells”) – and a high concentration of a compound called EGCG – is possibly beneficial to both preventing and potentially treating autoimmune disorders.
7. Fortified Cereal (Vitamin D)
Fortified cereal is a potentially rich source of vitamin D, and an excellent choice of vegans and vegetarians. Just one small serving of cereals containing enriched bran, fortified whole grain, and raisin bran have between 12 to 13 percent of recommended daily value (or RDI) for vitamin D.
Fatty fish, dairy products, orange juice, soy milk, and cheese are some other good sources of vitamin D. But without a doubt the best source of vitamin D is good old-fashioned sunshine!
8. Coconut Milk
People with an autoimmune disorder know better than to go crazy with milk (or any other dairy product, for that matter). Enter coconut milk, which has both pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory properties. Various studies have found that coconut milk helps to reduce inflammation and swelling, heal ulcers, and neutralize bacteria and viruses.
Foods To Avoid
Before we conclude, here are some foods for people concerned about an autoimmune disorder – or chronic inflammation in general – to consider limiting or avoiding (called the “AIP” or autoimmune protocol diet, the recommendations are quite strict):
- Alcohol
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Grains
- Legumes
- Sugary drinks or foods
- Nightshade veggies
- Cooking oils